Search engines work by following a simple process:
Crawl → Index → Rank
First, search engines send out bots to discover content across the web. Then they organize everything into a massive, searchable database. Finally, they use hundreds of signals to determine which results best match your query and show them in search results.
In this guide, I'll show you exactly how each step works and why it matters for your website.
But first, let's make sure we're on the same page.
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is an online tool that helps you find information on the internet. The most well-known example is Google.
In recent years, new AI-powered search engines have entered the scene, most notably Perplexity and ChatGPT Search. These work differently from traditional search engines; they use large language models (LLMs) to provide direct, conversational answers.
AI search engines don't hold an overwhelming share of the search market yet. According to Traffic Analytics data, google.com attracted 5.8 billion unique visitors in July 2025, while chatgpt.com received 651 million visitors:
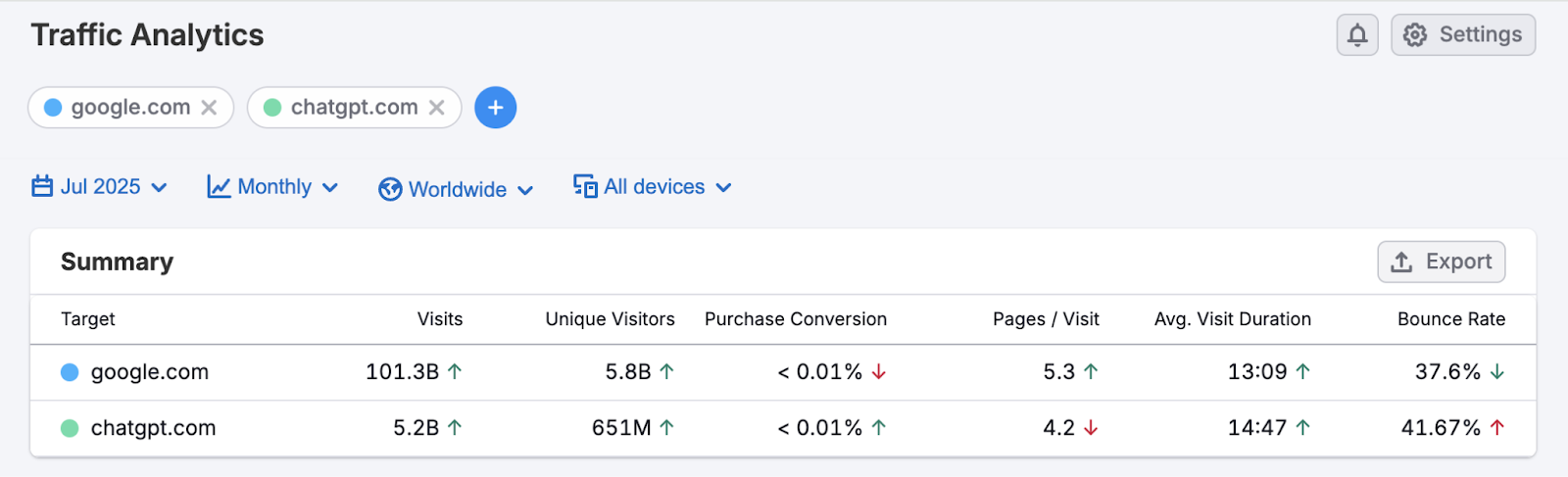
So, while AI search engines are gaining traction, traditional search engines are still the default for most users—especially when it comes to finding websites, shopping, or exploring the vast amount of information on the internet.
For that reason, this guide will focus exclusively on how traditional search engines work.
Why Is Understanding How Search Engines Work Important?
Understanding how search engines work is important in marketing because it helps you see how webpages like yours can get surfaced in search results.
On the flip side, if you don’t know their inner workings, you’re leaving your rankings up to luck. Or blindly following best practices without truly understanding them.
Trying to get your site show up in search engine results is called search engine optimization (SEO).
A lot of businesses make SEO a top priority because:
- The traffic you get from search engines is basically free
- Once you’re ranking well, that traffic tends to stay steady month after month
- Strong search visibility builds trust and brand authority over time
- People who search are already looking for what you offer—so they’re likely to convert (via a purchase, signup, or your preferred customer action)
For example, at Semrush, we’ve put a lot of effort into SEO over the years, and now we get close to 11 million unpaid visits from search engines every month.
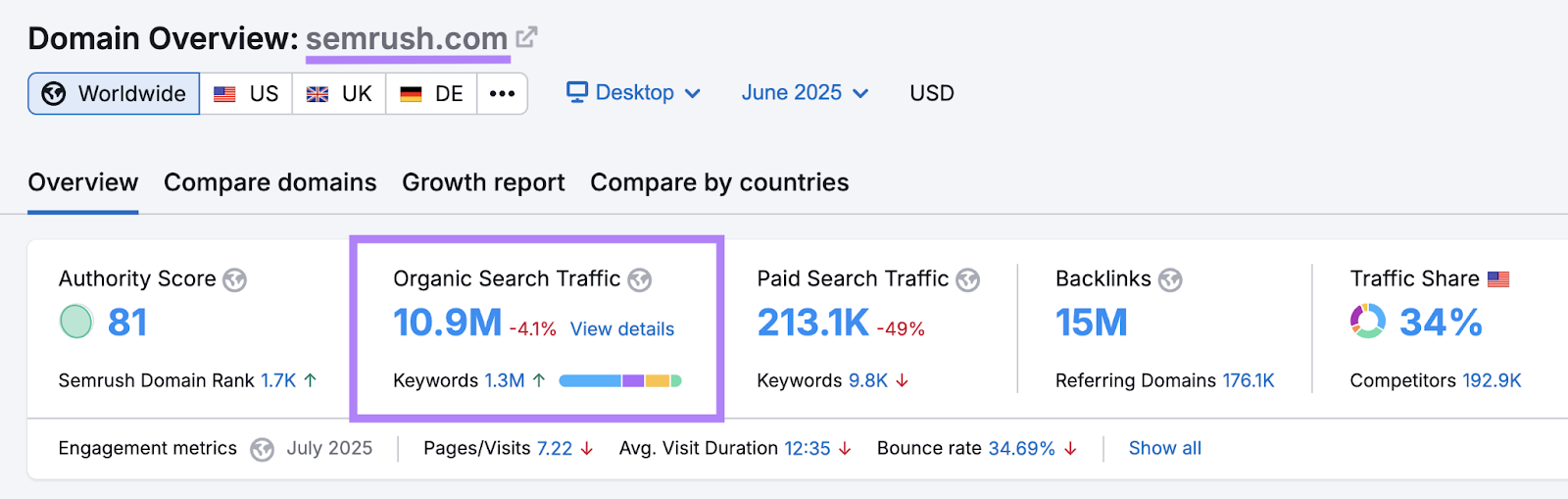
So it’s worth understanding how search engines work. Let’s get into it.
How Search Engines Work (Step by Step)
When you search on Google, it feels instant. You hit enter, and boom—millions of results in under a second.
But search engines don't "search the web" in real-time. They've already done most of the heavy lifting ahead of time by continuously crawling, indexing, and organizing the web into a massive, searchable database.
Let’s break that down.
1. Crawling: Finding Content on the Web
Crawling is a process by which search engines find what exists on the web.
They use computer programs (called bots, robots, or crawlers) to systematically browse the web 24/7. These bots start with a list of known webpages and follow links from those pages to discover new content.
Google’s crawler, Googlebot, is probably the most famous, but every search engine has their own version. These bots work nonstop, constantly discovering new pages, revisiting existing ones to check for updates, and mapping the ever-changing landscape of the web.
During crawling, the bots download the content of each page they visit—the text, images, videos, and links—so the search engine can analyze and understand it later during indexing.
2. Indexing: Adding Content to the Search Database
Once a crawler discovers and downloads a page, the search engine needs to make sense of what it found. This is where indexing comes in.
Indexing is essentially the process of organizing and storing all that crawled content in a massive, searchable database (the “index”).
During indexing, search engines analyze each page to understand:
- What the page is about (the main topic and themes)
- What type of content it contains (text, images, videos, etc.)
- How it's structured (headings, paragraphs, lists)
- What keywords and phrases it targets
- How it relates to other pages on the web
Not every crawled page gets indexed. Search engines may skip pages that are duplicate content, are blocked by noindex tags, or provide little value to users.
3. Ranking: Displaying Results in the Best Order
When you type a query into a search engine, this is where the magic happens. The search engine doesn't actually search the entire web in real-time—that would take forever. Instead, it searches through its index to find the most relevant pages.
The search engine uses complex ranking algorithms to determine which pages best match your query and in what order to display them.
Within milliseconds, the search engine compiles a ranked list of results and displays them on the search results page, often along with additional features like direct answers, images, and videos.
More recently, traditional search engines like Google have started integrating AI-generated summaries (like the AI Overview feature) at the top of search results. These pull from multiple sources and try to answer your question directly, without requiring you to click.
AI is definitely changing how search engines surface information, but the core steps—crawling and indexing—are still the foundation of how it all works.
How Google’s Search Algorithm Works
Google’s ranking algorithm is designed to surface the most relevant and high-quality information to its users.
To do that, it looks at:
- Meaning of the query – Google tries to infer the meaning of the query to understand what exactly the user is searching for
- The relevance of pages – How relevant are the pages in Google’s index to the searched query? This includes looking at the title, headings, and actual content of the pages.
- Quality of content – Google looks at the quality of content to pick the best results for a query
- Usability of pages – Google also looks at the loading speed and mobile compatibility of pages
- Location and search history – The user’s location and history of searches are also considered
Google is always tweaking its algorithms, with small changes happening daily and bigger “core updates” a few times a year. These core updates are officially announced and always get the SEO community talking.
As for the actual ranking factors, most of the important ones are public knowledge.
Search Engine Ranking Factors
Let's look at some important Google ranking factors (in no particular order):
- Loading speed: Fast-loading pages provide a better user experience. Google favors them.
- Quantity and quality of backlinks: This signals to Google that your content is worth ranking higher because other sites are willing to reference and recommend it to their own audiences
- Content that matches the user intent: Content that aligns with what the user is actually looking for—whether it's a quick answer, a detailed guide, or a product comparison—is more likely to rank well
- Keyword usage and on-page optimization: Proper use of keywords in headings, meta tags, and throughout the content helps Google understand what your page is about and show it for relevant queries
- Unique content: Google favors original content that provides a fresh perspective or new information on a topic
- Mobile-friendliness: Most searches happen on phones, so Google prefers pages that work smoothly on mobile devices
- Fresh content: Recently published or updated content often ranks better, especially for time-sensitive topics like news or trending subjects
Sergei Bezdorozhev, SEO & International Blogs Lead at Semrush, says:
Content quality is the big one—almost half of these key ranking factors are about content. And it makes sense. Every search engine wants to provide the best, most useful information to its users. And if they don't do it, people will stop using their service. It's that simple.
Google’s whole business model depends on delivering great results. So they’re constantly working to push pages to the top that truly deserve it. You can’t game the system anymore. Create great content—that’s the way to win.
Start Optimizing Your Website for Search Engines
Search engines represent a huge source of potential traffic for websites.
If you're a marketer or a business owner, you want to tap into this massive opportunity and invest in SEO as a core part of your growth strategy.
Semrush gives you a complete toolkit to plan, execute, and measure your SEO efforts—whether you’re just getting started or looking to improve an established site.
For example, our Keyword Magic Tool can pull up thousands of keyword ideas specific to your business, making it a lot easier to find the right keywords to target.
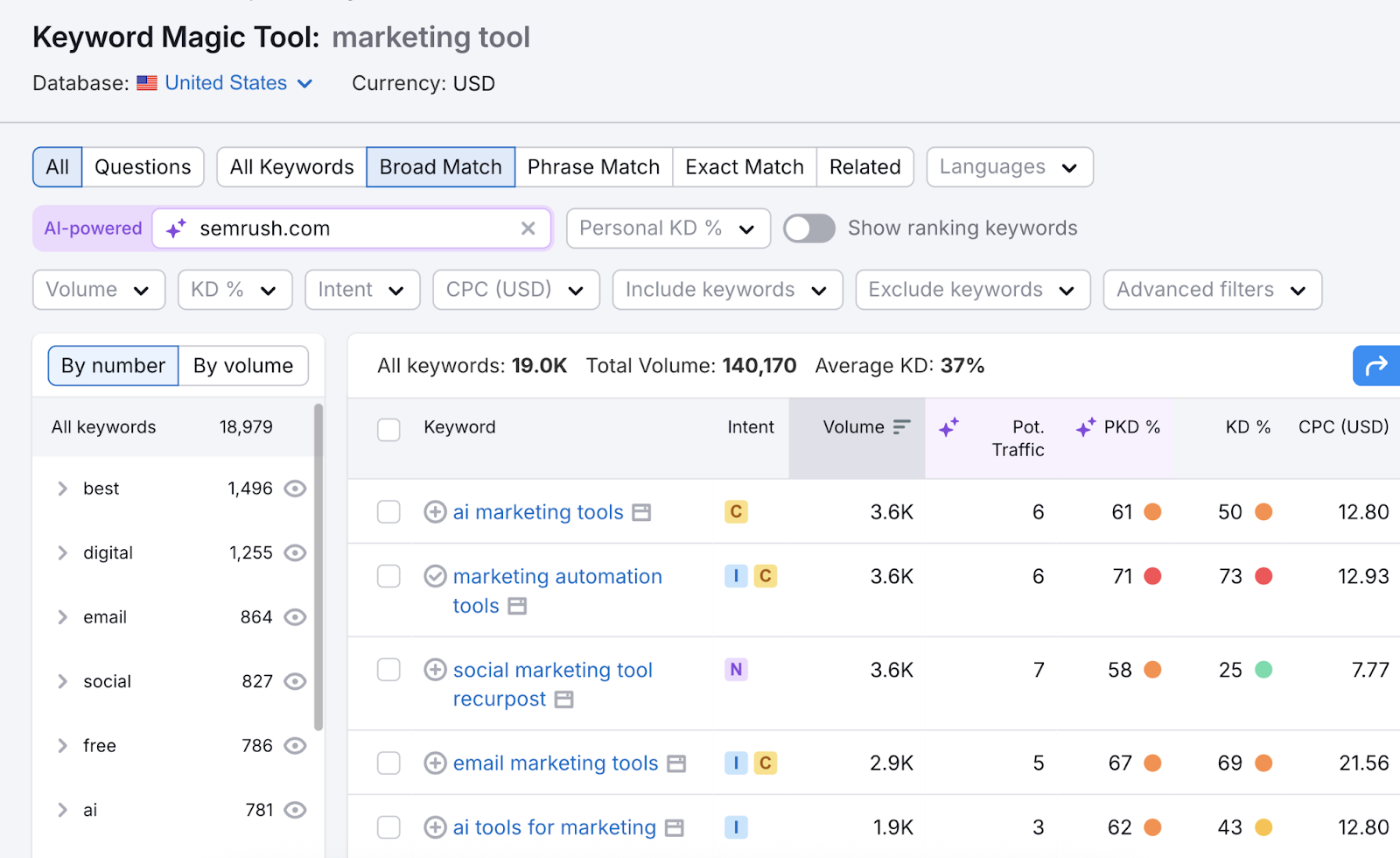
There are dozens of other tools in the platform that make doing SEO much easier.
Sign up today to get started.