Google’s AI Mode is live—and while it’s not yet dominant, the early behavior signals are worth watching.
Using a large, anonymized dataset from real users, we explored how users are adopting AI Mode and what that might mean for the future of search.
How often do the early adopters actually engage with AI Mode?
Is it pulling people away from traditional Google Search?
And what does this all mean for SEO and brand visibility?
This study unpacks:
- Daily usage patterns across AI Mode vs. traditional search
- The rise of longer, more conversational queries
- External traffic rates (spoiler: 92–94% of sessions are zero-click)
- How Google AI Mode adoption compares to ChatGPT
Methodology
Here’s how we ran the study:
- First, we took clickstream data for almost 69M Google Search sessions that happened between May 1 and July 5, 2025
- We only looked at sessions that happened in the U.S. on desktop devices
- We analyzed this dataset’s daily interactions with Google AI Mode by checking the number of daily searches and sessions, prompt length, and traffic to external domains
AI Mode Sees Steady Adoption in Its First Two Months
In the first two months since the rollout of AI Mode in May, the share of AI Mode usage among Google search sessions increased roughly 4x (from 0.25% in early May to a little over 1% by early July).
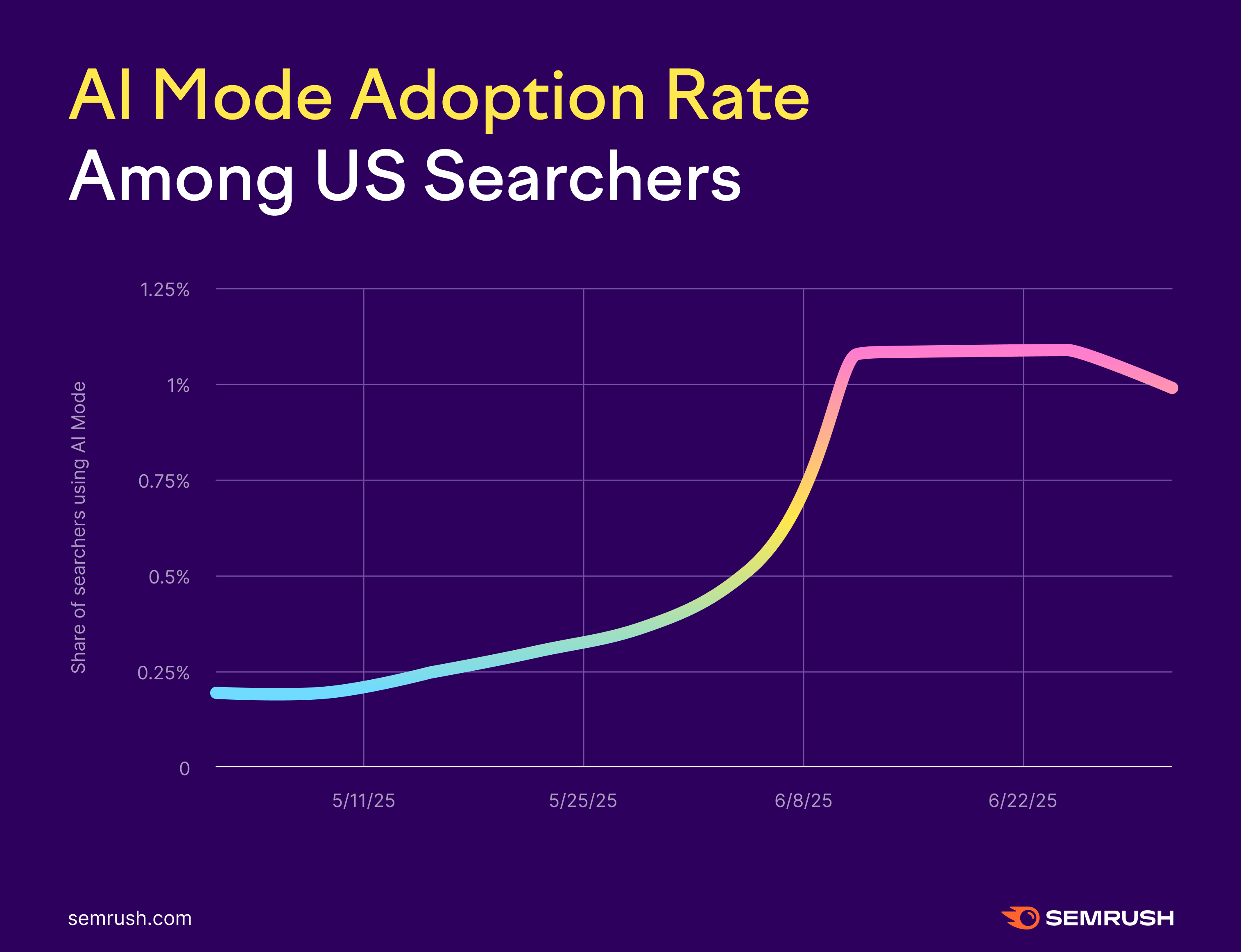
Some key dates to note:
- March 5, 2025: Google introduces its “experimental” AI Mode in AI Labs
- May 20, 2025: Google starts rolling out AI Mode in the U.S.
- June 27, 2025: Google officially launches AI Mode for all U.S. searchers
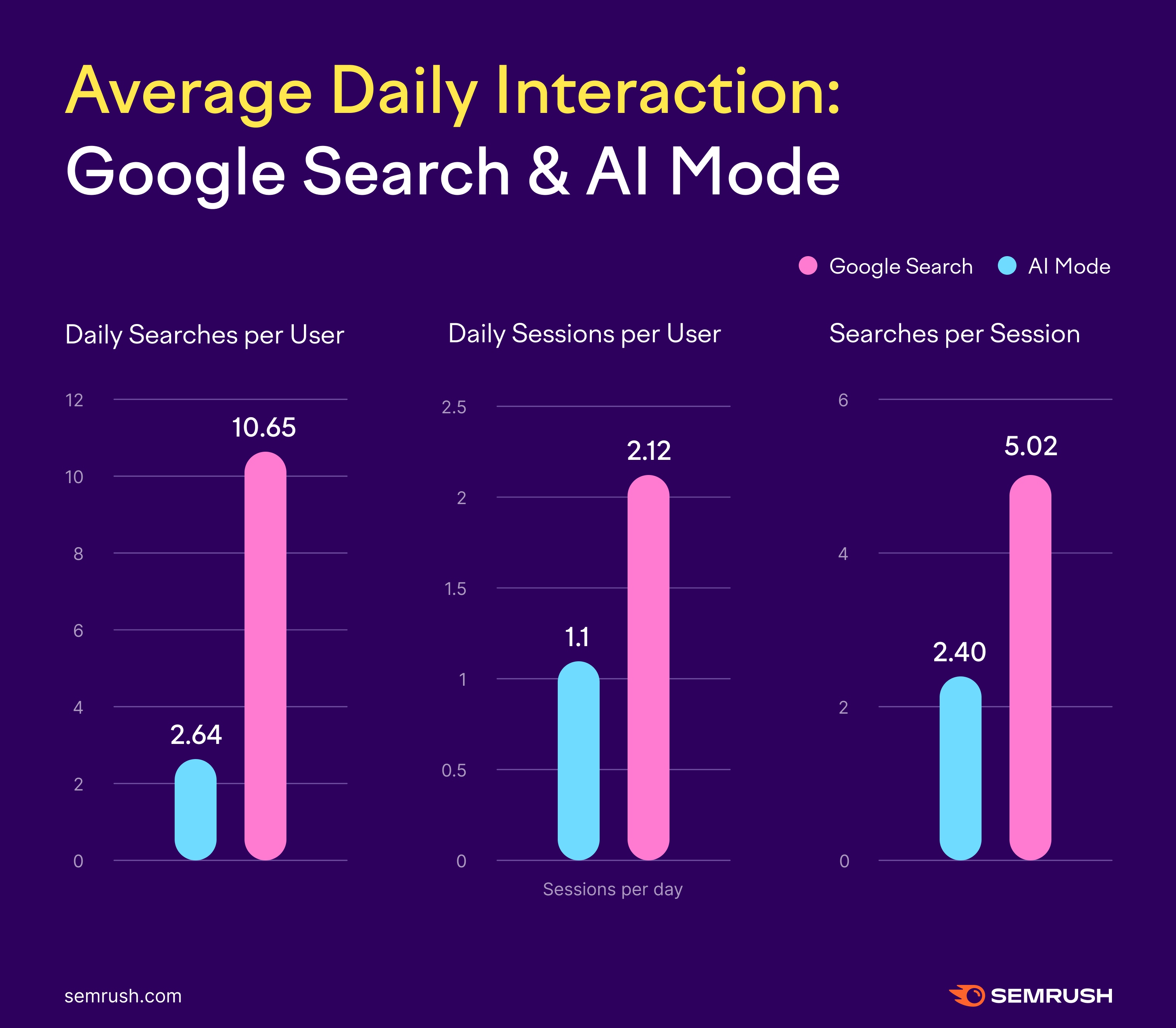
Average AI Mode User Makes About One Daily Session of 2-3 Queries
Compared to traditional Google Search, people had fewer daily sessions and fewer searches per session on AI Mode.
What might this mean?
It tells us that people are using Google and entering an initial search, only to then go back and change the query or search for something else five times before finally finding what they’re looking for.
In other words, there’s some trial and error.
On AI Mode, the average session only took between 2-3 searches. So the back-and-forth is resolved in half as many queries.
Throughout our period of research, these rates didn’t grow but remained pretty stable.
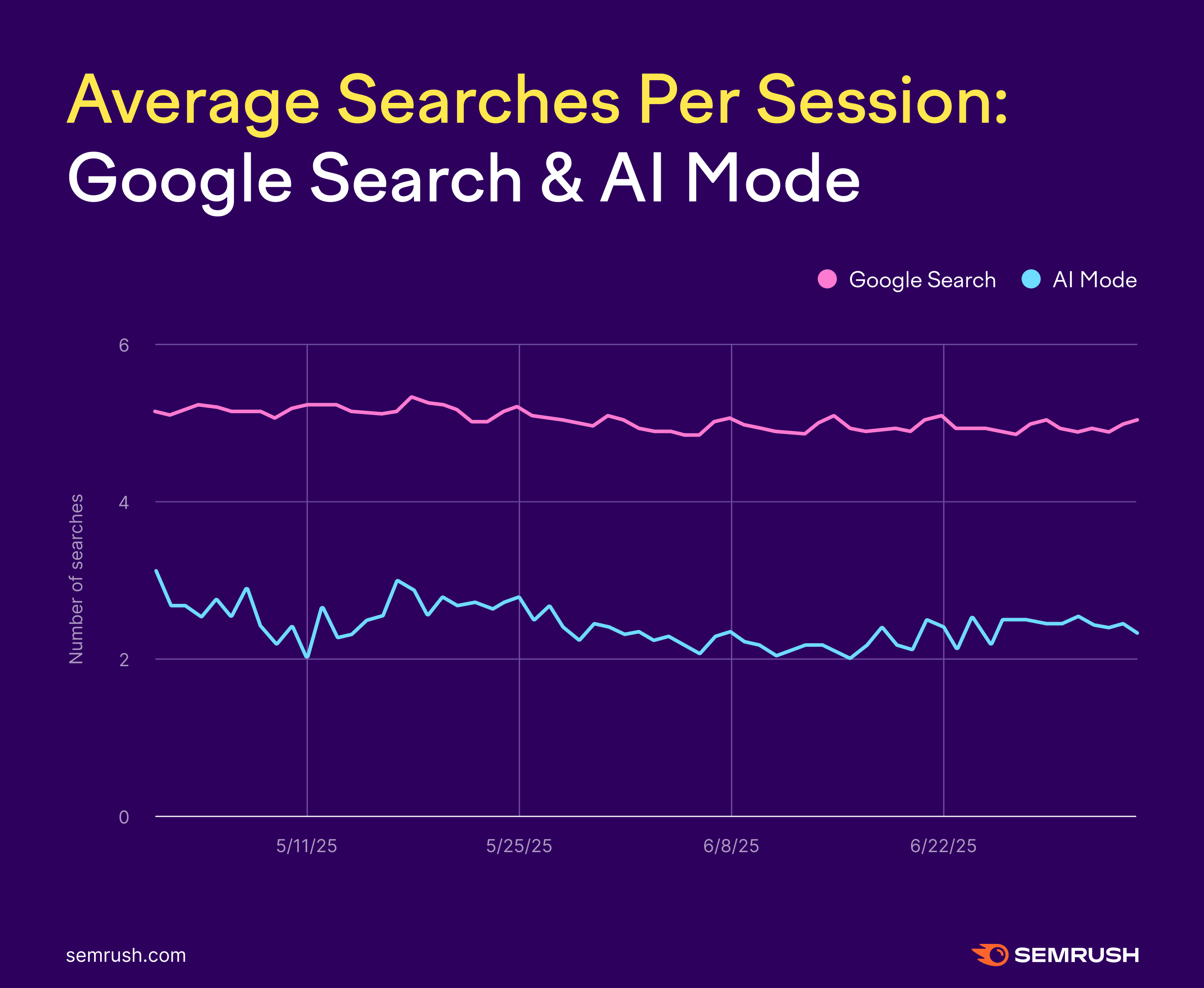
It’s still very early, but this tells us that most users are steady in their adoption.
Considering this is just the first two months after its launch, adoption is likely to grow as Google pushes more users toward AI Mode.
As AI Mode usage grows, it will be interesting to watch if the number of searches per session on AI Mode remains below the average for traditional search.
One of the strengths of AI Mode is that it can understand and process longer, more complex questions than traditional search. So, it makes sense that it could resolve a search session in fewer total queries.
As people get familiar with how it works, we could see even more AI Mode sessions resolving with fewer (but longer and more detailed) queries than traditional search.
So Far, AI Mode Sends Minimal Traffic to External Domains
From our clickstream sample, we saw that, on average, 6-8% of AI Mode sessions led to someone visiting an external domain.
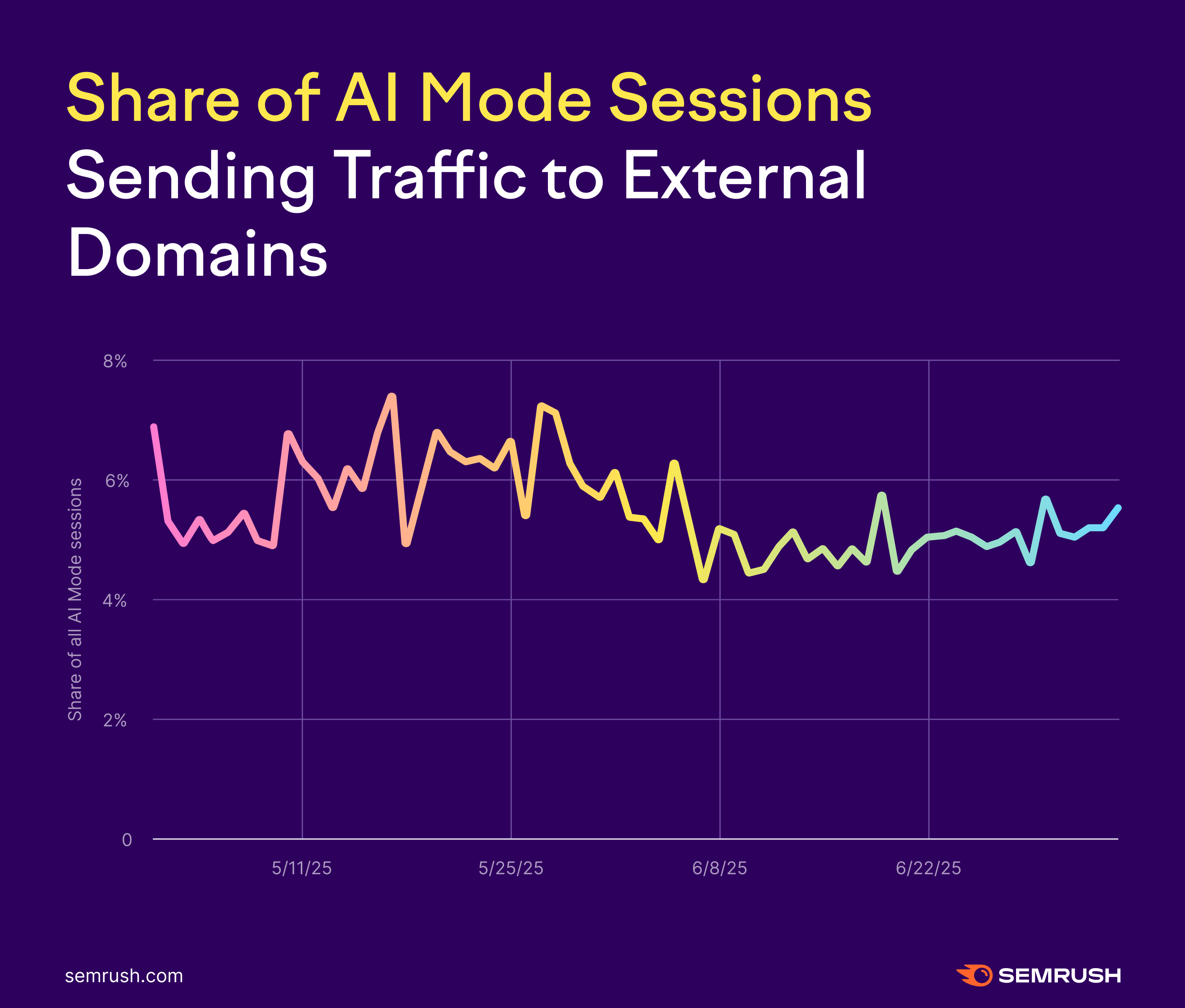
That means 92-94% of AI Mode searches were zero-click searches.
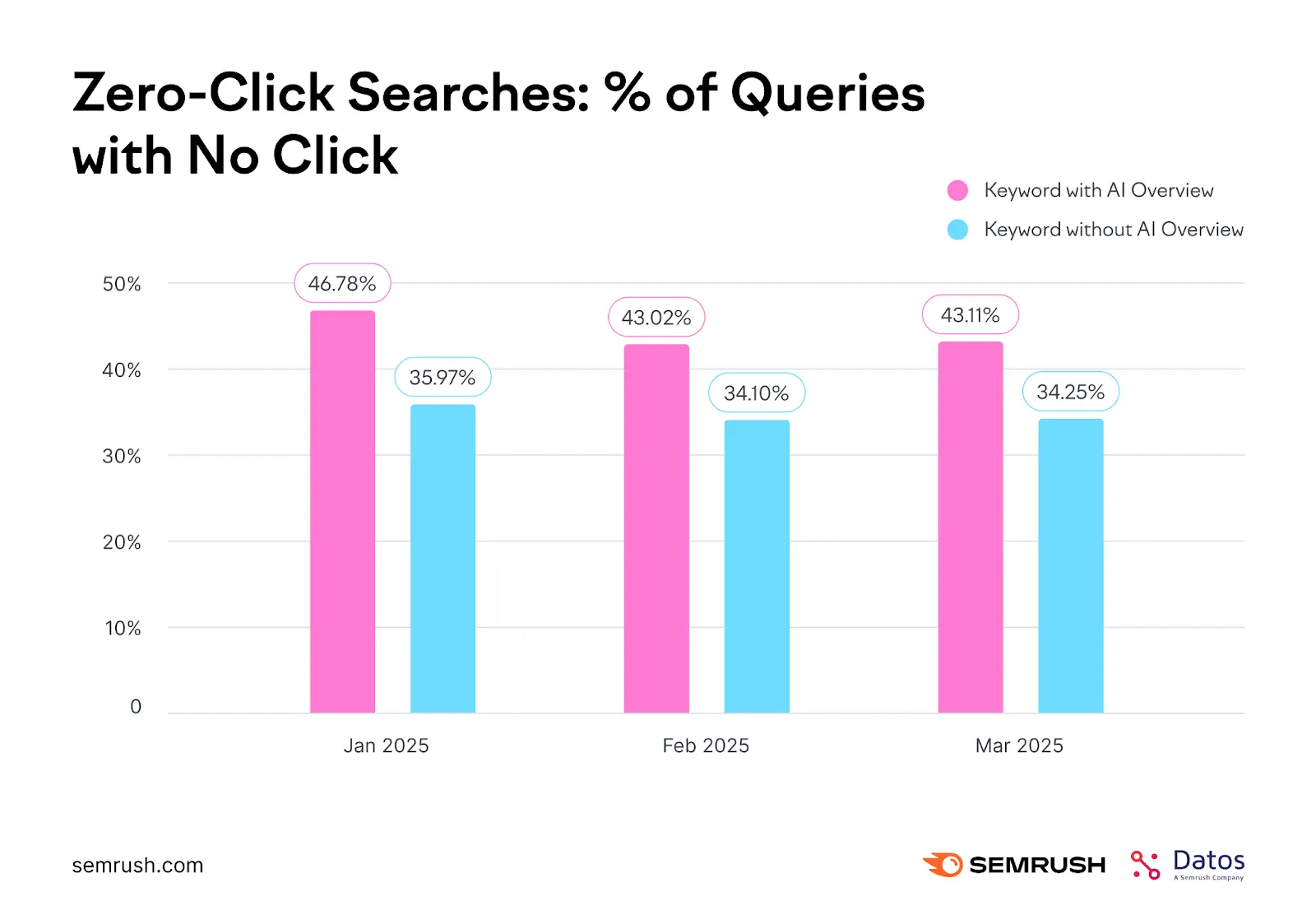
That’s much higher than the average on Google Search. According to our study of Google Search and AI Overviews from earlier in the year, the typical rate of zero-click searches was between 35-46%, depending on the presence of an AI Overview or not.
While direct comparisons should be made with caution, the overall trend is consistent: As Google integrates more AI-driven responses, the likelihood of users clicking through to external sites declines.
- Google Search without AI Overview: ~34% zero-click
- Google Search with AI Overview: ~43% zero click
- Google AI Mode: ~93% zero click
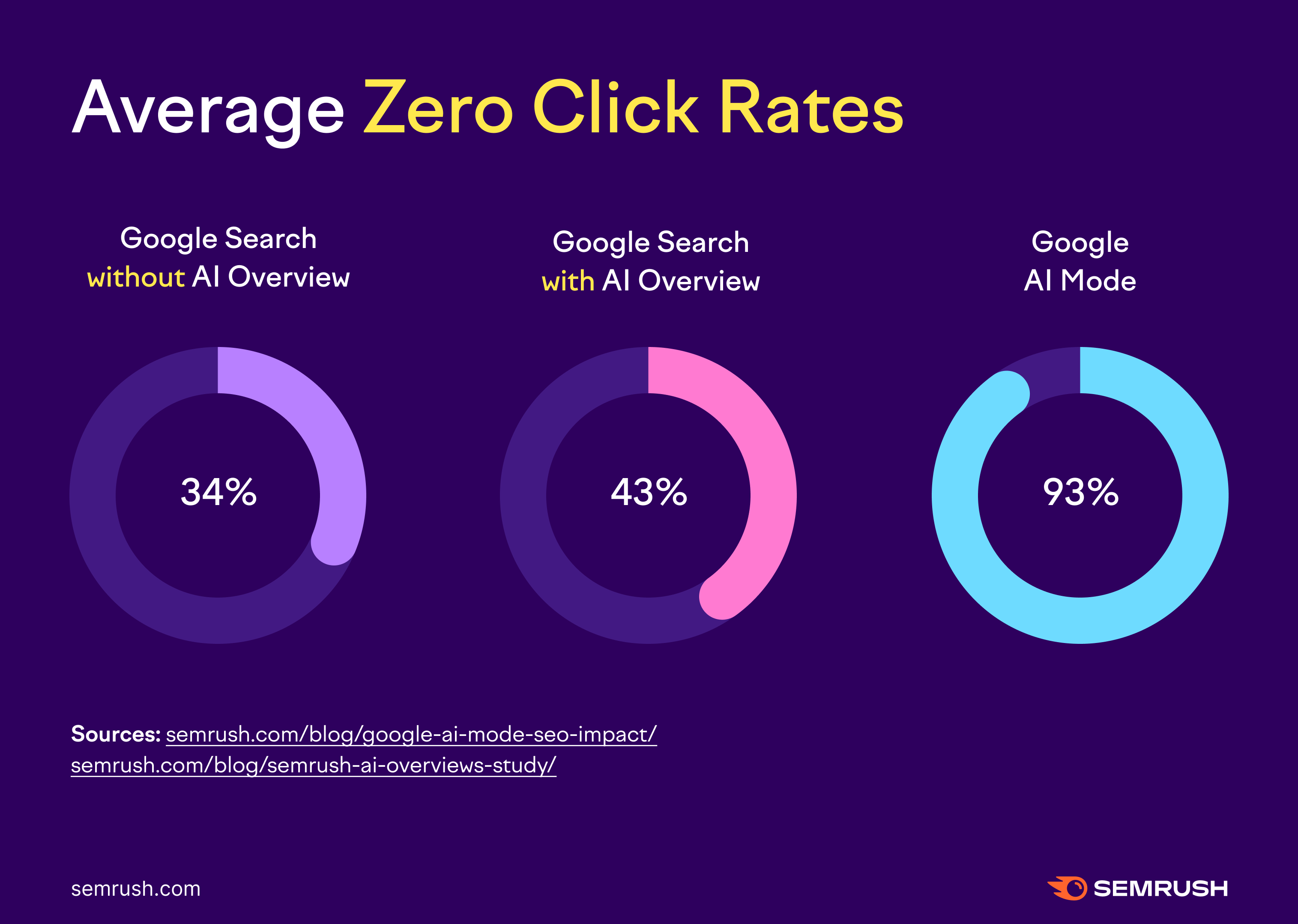
Note: The zero-click percentages cited here come from separate studies, each using different methodologies and timeframes.
As zero-click experiences rise and attribution becomes murkier, measuring the impact of SEO and content efforts will only get harder—making brand visibility within AI answers more critical than ever.
In a recent AI Search Semrush Webinar, Barry Schwartz highlighted how traditional metrics like clicks and conversions are becoming less reliable due to AI answers.
You’re not going to see traffic from AI unless you’re measuring brand mentions and sentiment in those answers. It’s billboard SEO now. How do we measure billboards? How do we measure radio ads? It’s the same thing. You look at overall visibility, brand mentions.
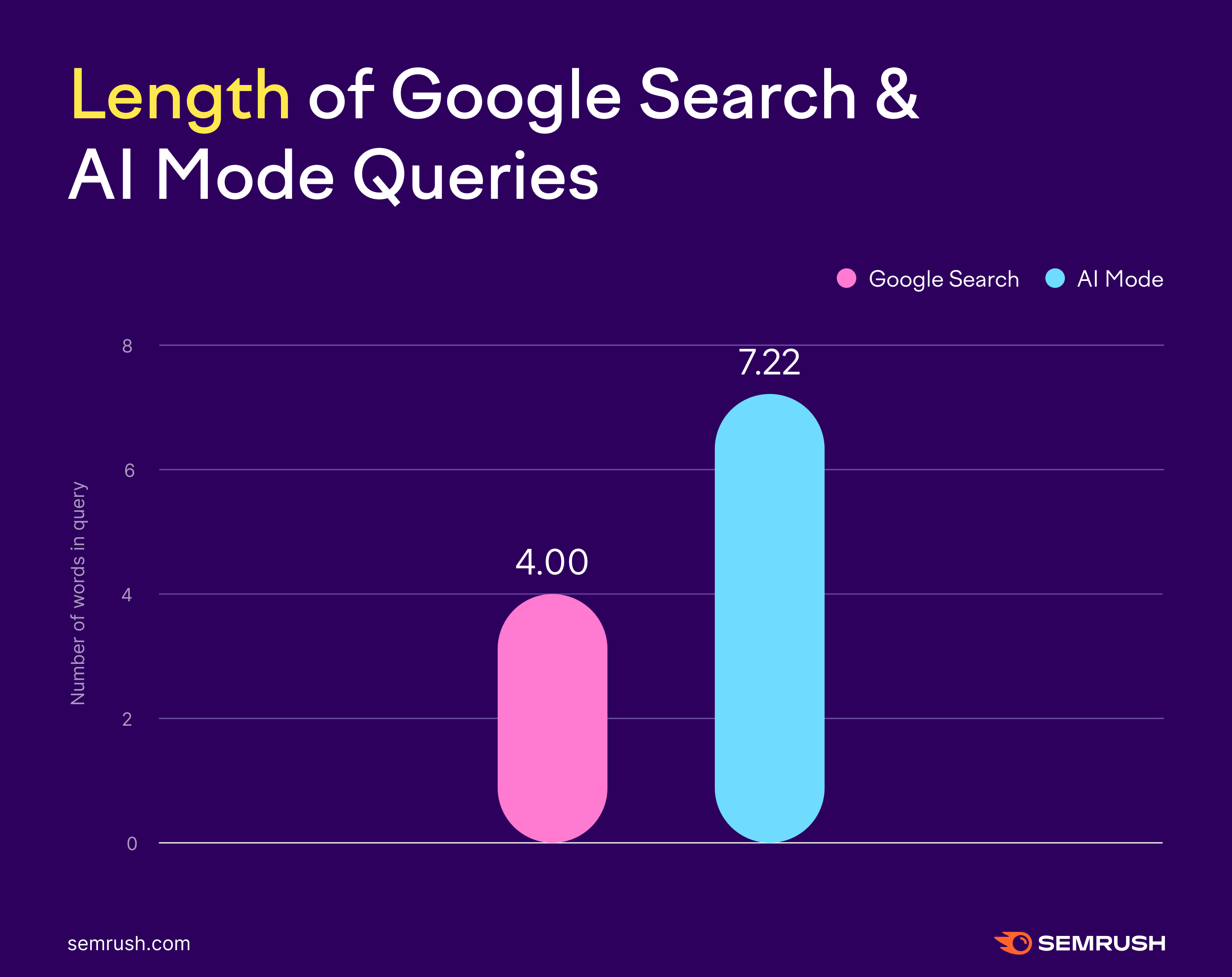
Average AI Mode Query Length vs. Traditional Google Search
One way of understanding how people use AI Mode is by query length.
Do people treat AI Mode more like traditional search or ChatGPT?
In our study, the average AI Mode query was almost twice the length of a traditional query (7.22 words vs. 4.0 words).
To compare this to ChatGPT (and ChatGPT Search), let’s look at a previous Semrush study.
In a February 2025 study, we looked at the prompt lengths on ChatGPT vs. ChatGPT Search (SearchGPT) and noticed a huge difference in prompt length when users had the “SearchGPT” feature on/off.
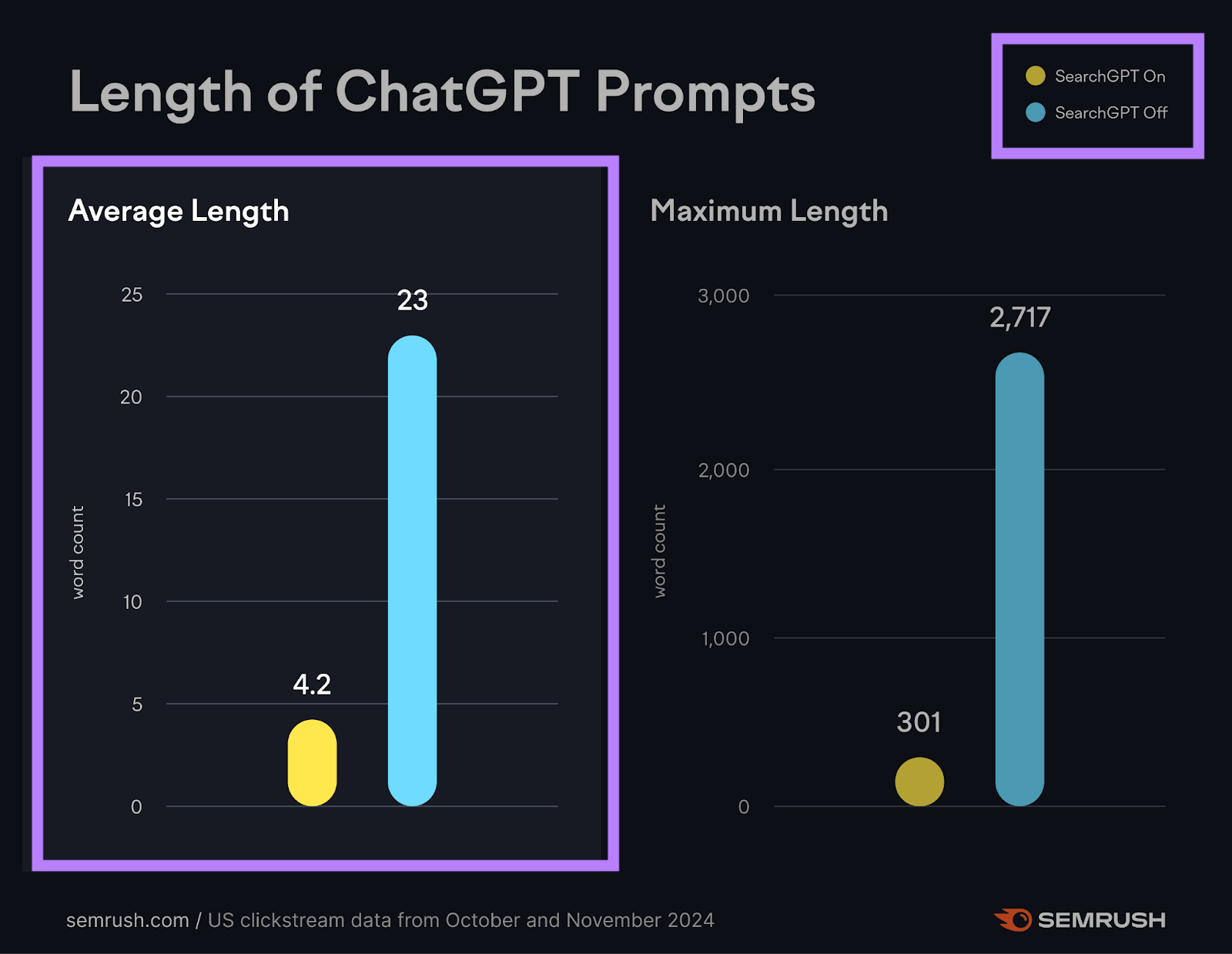
When people interact with an AI chatbot (ChatGPT), they write longer queries.
When they’re interacting with a “search” interface (like ChatGPT Search or Google Search), the queries get shorter—around four words per query.
AI Mode landed somewhere in between ChatGPT and Google here.
The Implication of Longer Queries
The average Google search query is about four words.
“Best plumber near me,” “used car for sale,” and “feeding chart for babies” fit the form.
On AI Mode, the queries stretch out a little.
With seven words, there’s more room for more conversational and detailed queries.
Like:
- “Low cost plumbing for seniors near me”
- “Safest and most affordable car for teenagers”
- “Best practices for feeding routine for babies”
You can enter more modifiers and include more context with a longer query. But people won’t give Google Search a 23-word query, because they don’t trust it to handle it in the way ChatGPT might.
Average query length signals how users mentally “position” the tool they’re interacting with.
The longer the input, the more personal, complex, and conversational the intent.
- Google Search (four words): People rely on short, telegraphic queries that resemble commands. They assume minimal context and expect a list of links.
- AI Mode (seven words): A shift toward full-sentence questions resembling a question you’d ask another person. This query type expects a slightly more tailored, synthesized response, not just results.
- ChatGPT (23 words): People treat the system like a collaborator. Prompts are detailed, goal-oriented, and often include lots of context, constraints, or roles to expect a personalized output.
| Query length | Examples | Goal |
| Four words |
| Finding a list of options or sources to investigate deeper on external sites. |
| Seven words |
| Asking for a curated, up-to-date list of options for a specific context. |
| 20+ words |
| Getting a comprehensive solution that accounts for even more detailed context and personal preferences. |
How Google Wants People to Use AI Mode
In its promotional announcement, Google featured a 26-word query as their featured example (see below).
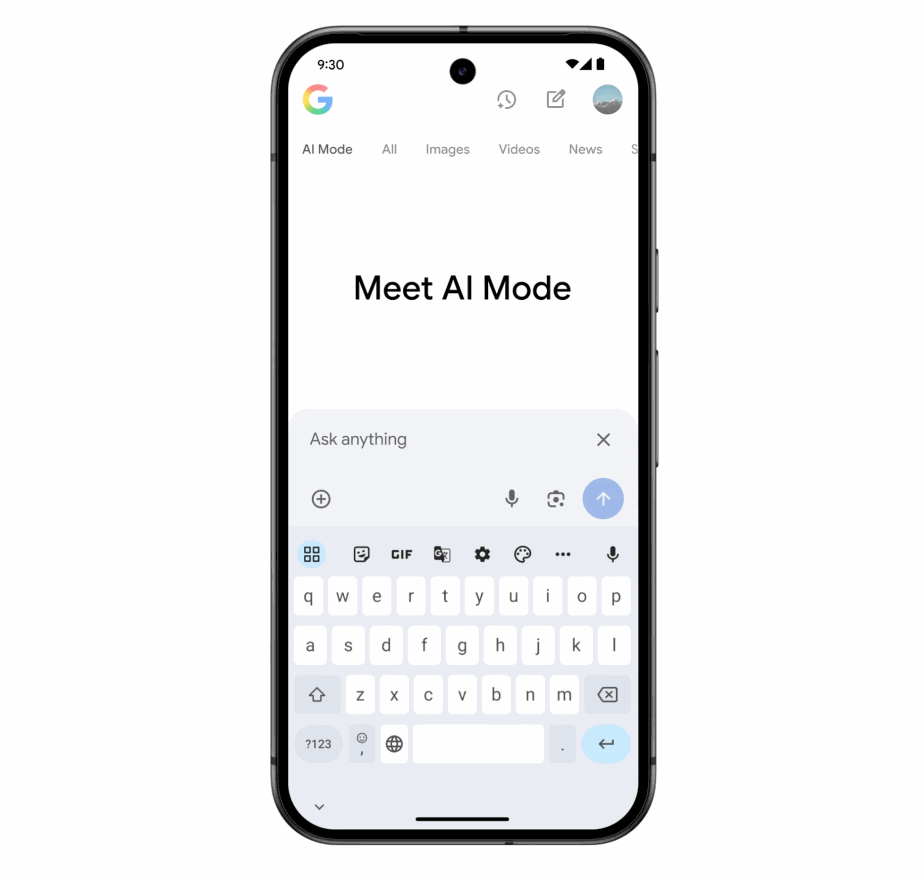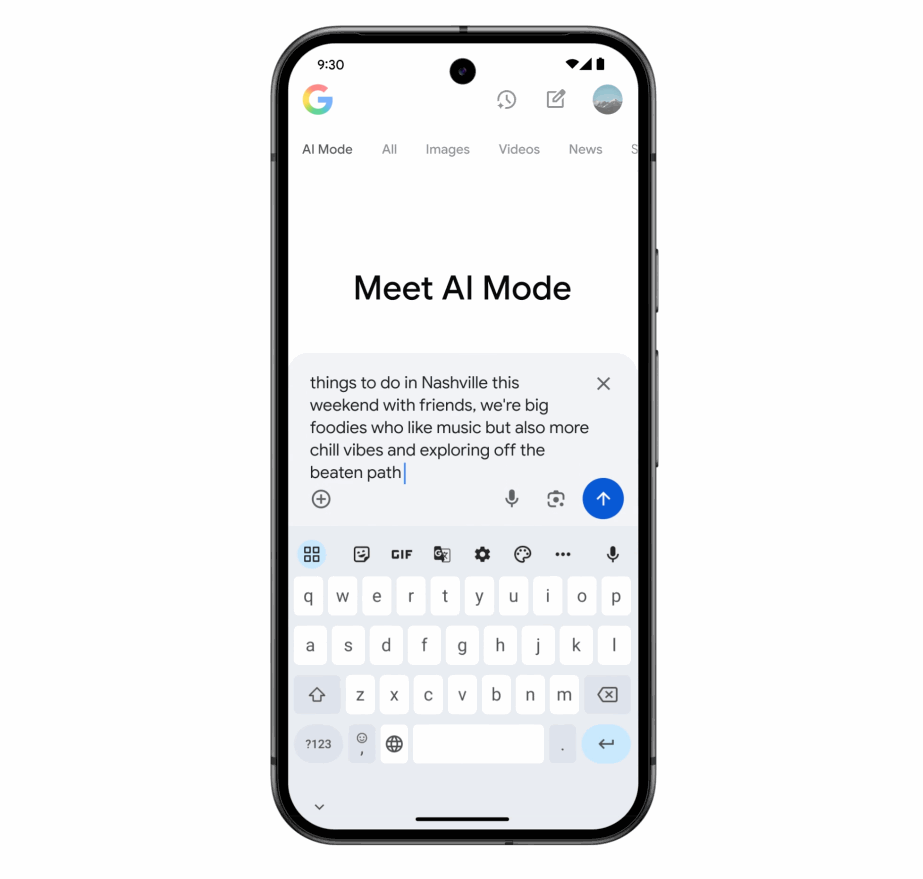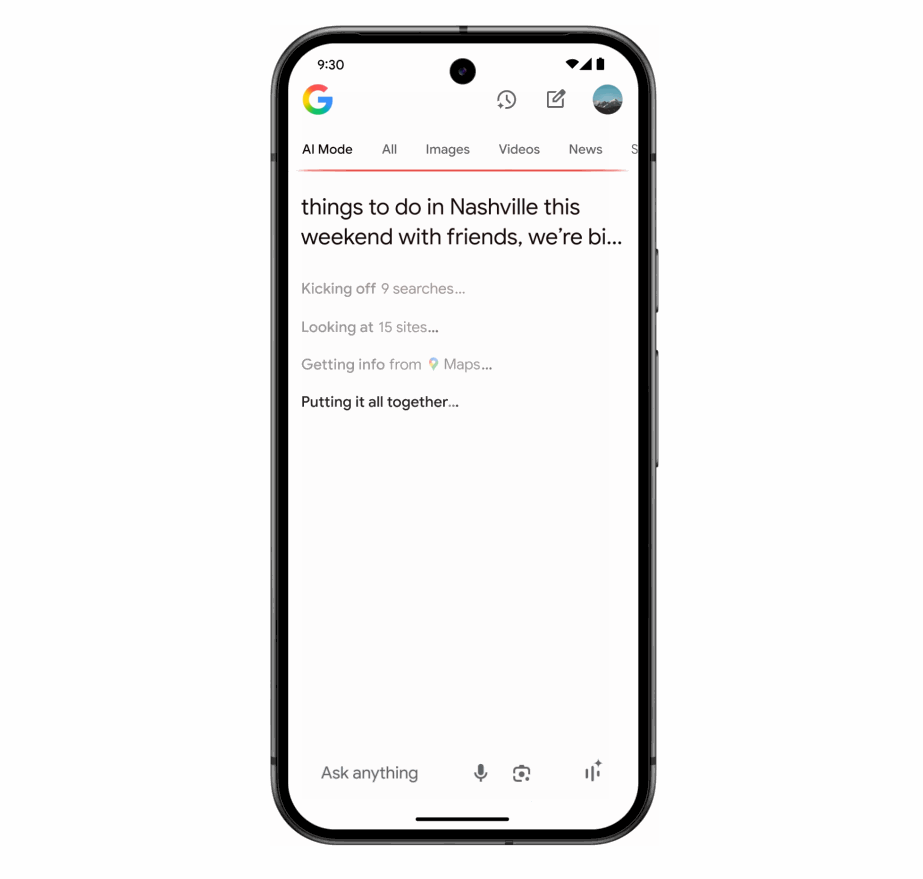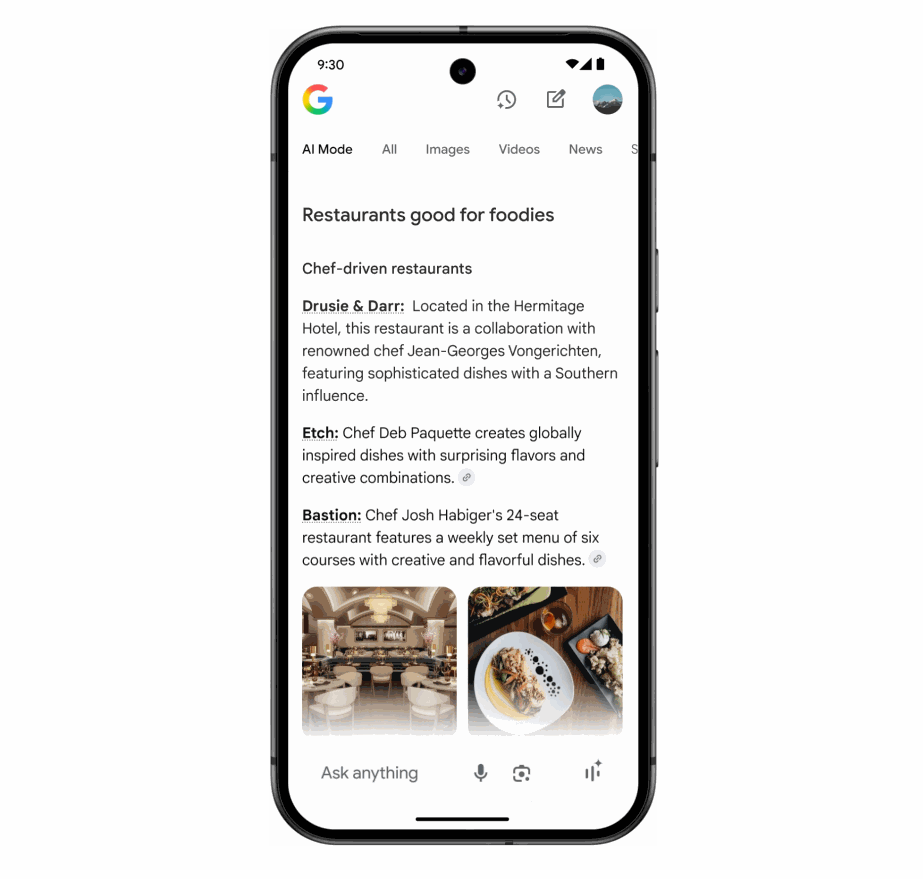
This could mean that this longer, context-rich query style is what the company is planning to achieve among AI Mode users.
With the query fan-out technique, AI Mode should be able to handle these contextual queries by running multiple concurrent searches across the subtopics of a single query.
In its documentation, Google claims this fan-out “helps you access more breadth and depth of information than a traditional search on Google.”
What used to take multiple Google searches to get the right answer can be answered with a single AI Mode query.
That trend was reflected when we saw fewer searches per session on AI Mode compared to traditional search.
Somewhere Between Google Search and ChatGPT
AI Mode works like an AI assistant, but most users still treat it like a search engine—offering short, traditional queries instead of detailed prompts.
That behavior will likely evolve.
Google plans to bring AI features into core search, and users are already being nudged toward more conversational habits.
Search Engine Land recently reported seeing conversions starting to grow among slightly longer queries.
Does this show how people are slowly being trained toward entering more long-form queries into search, as everything grows more AI-powered?
Marketers shouldn’t wait.
To stay visible, content strategies should adapt to:
- Grow your topical authority by covering entire topics (not just keywords) from multiple intents and contextual angles
- Establish your brand’s unique value proposition to stand out from your competitors
- Structure content to get cited in AI-generated answers, not just achieve traditional rankings
Bottom line: You want to show up in context—not just in rankings.
AI Mode Is Shaping the Future of Search—and SEO
Early AI Mode adopters are experimenting, but not yet fully committing, to long-form conversational interactions like they do with ChatGPT.
And while AI Mode does send traffic out—about 6-8% of sessions include an external click—it’s still overwhelmingly a zero-click experience.
However, with Google’s plans to keep pushing in the direction of AI-powered search and discovery, marketers can’t afford to ignore it.
To track how your brand shows up in AI Mode, Semrush offers some great options:
- Track target keywords in AI Mode with Position Tracking
- Measure overall sentiment, visibility, and share of voice within AI Mode with the AI Toolkit
- Follow AI Mode and AI Overviews at the Enterprise level with Semrush Enterprise